External Rotation in Abduction: Exploring its Importance in Orthopedics and Physical Therapy
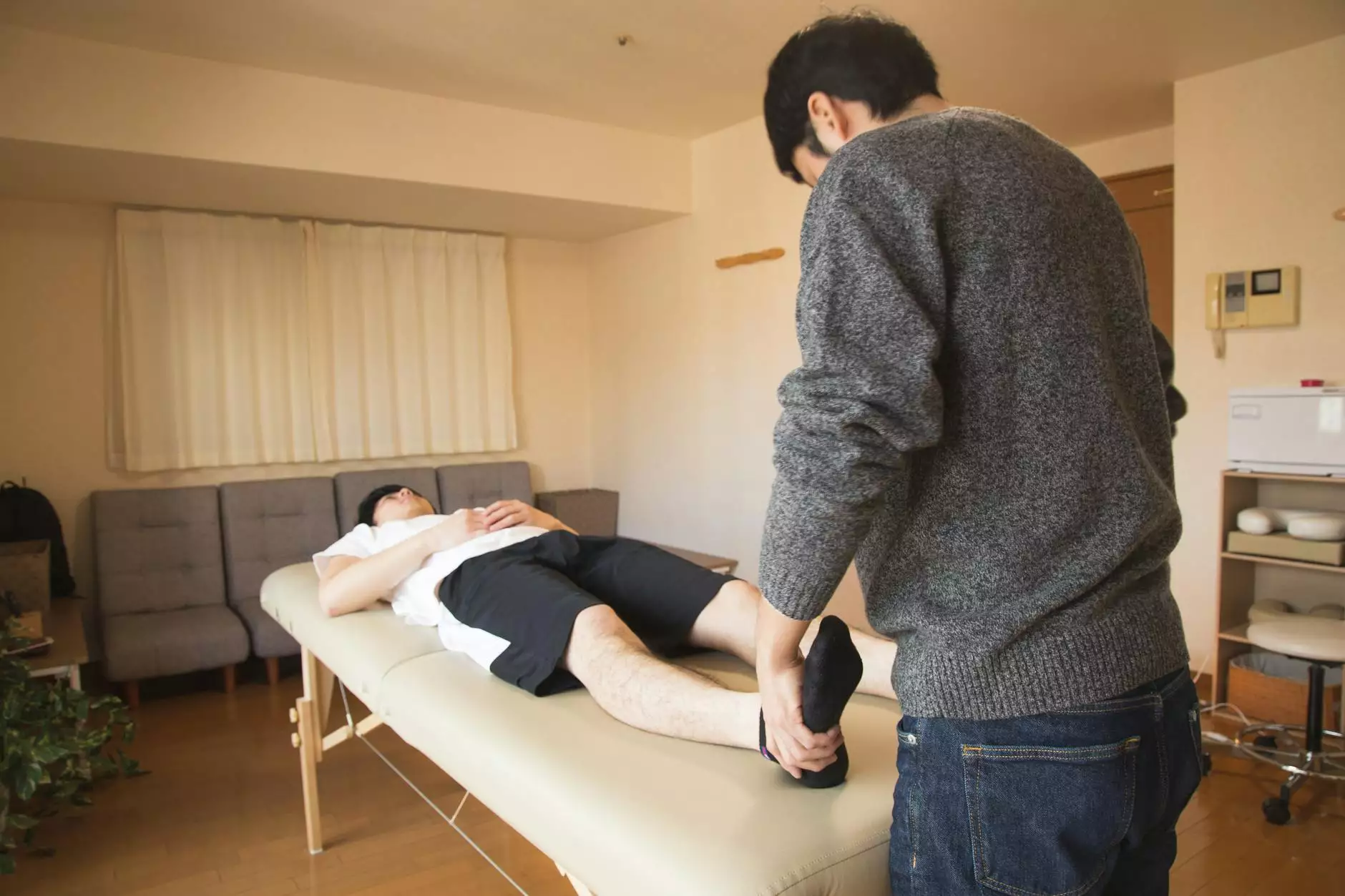
Introduction
In the realm of orthopedics and physical therapy, precise terminology is crucial for effective communication and understanding. One such term that holds significance is "external rotation in abduction." This article aims to delve into the depths of this expression, exploring its importance and utility in the fields of orthopedics and physical therapy. Throughout this comprehensive guide, we will uncover its definition, its relevance in rehabilitation and assessment, and discuss its implications for practitioners.
Understanding External Rotation in Abduction
External rotation in abduction refers to a particular movement or position of a body part, typically a joint, where the joint rotates outward while the limb is moved away from the body. This motion involves the muscles, tendons, and ligaments surrounding the joint, allowing for both stability and mobility in various activities.
Primarily used within the orthopedic and physical therapy realms, external rotation in abduction plays a significant role in injury assessment, rehabilitation, and functional movement analysis. By understanding this movement, practitioners can develop tailored treatment plans and exercise regimes to address specific musculoskeletal issues.
The Role of External Rotation in Abduction in Orthopedics
In the orthopedic field, external rotation in abduction holds particular importance, as it allows clinicians to evaluate and diagnose certain conditions. By assessing the range and quality of this movement, practitioners can gather valuable information about a patient's joint function, identifying any abnormalities or limitations therein.
Various orthopedic conditions, such as shoulder impingement syndrome, rotator cuff tears, and glenohumeral instability, can be diagnosed using external rotation in abduction. Furthermore, this movement assists in identifying muscle imbalances, joint laxity, and other dysfunctions that may contribute to chronic pain or decreased range of motion.
External Rotation in Abduction and Physical Therapy
In the realm of physical therapy, the utilization of external rotation in abduction is paramount. Therapists employ this movement as both an assessment tool and a rehabilitative exercise to restore and enhance joint function. By analyzing the performance of this movement, physical therapists gain insights into potential muscular imbalances, weaknesses, or compensatory mechanisms triggered by injuries or surgeries.
During the rehabilitation process, physical therapy often involves exercises aimed at improving external rotation in abduction to enhance joint stability, increase range of motion, and improve overall physical performance. These exercises may include resistance training, stretching routines, and functional movements that stimulate specific muscle groups.
Rehabilitation and Assessment Purposes
External rotation in abduction is extensively utilized in both rehabilitation and assessment settings in orthopedics and physical therapy. When working with patients recovering from orthopedic surgeries or injuries, therapists conduct various examinations to gauge progress and identify potential limitations.
Assessment of external rotation in abduction can provide therapists with valuable data to determine the effectiveness of treatment protocols, predict recovery timeframes, assess the return to functional activities, and measure overall rehabilitation success. By precisely measuring and documenting these movements, practitioners can track improvements over time and adapt treatment plans accordingly.
Importance of Proper Technique and Guidelines
While external rotation in abduction is an invaluable tool within orthopedics and physical therapy, it is vital to highlight the significance of proper technique and adherence to guidelines. As with any exercise or assessment, incorrect form or excessive strain may lead to further injury or complications.
It is imperative for orthopedic practitioners and physical therapists to ensure that patients perform external rotation in abduction exercises correctly. This includes appropriate patient positioning, utilizing proper resistance or assistance, and providing clear instructions to avoid unnecessary strain or injury to the joint or surrounding structures.
Conclusion
External rotation in abduction is an essential term within the world of orthopedics and physical therapy. Its significance lies in its ability to assess, diagnose, and rehabilitate various musculoskeletal conditions. Through a comprehensive understanding of this movement, practitioners can develop targeted treatment plans, aid the recovery process, and promote optimal joint functionality.
As practitioners continue to explore the intricacies of external rotation in abduction, it is crucial to stay up-to-date with research, advancements, and evolving practices. By doing so, orthopedic experts and physical therapists can further enhance their ability to provide effective care and positively impact patients' lives.